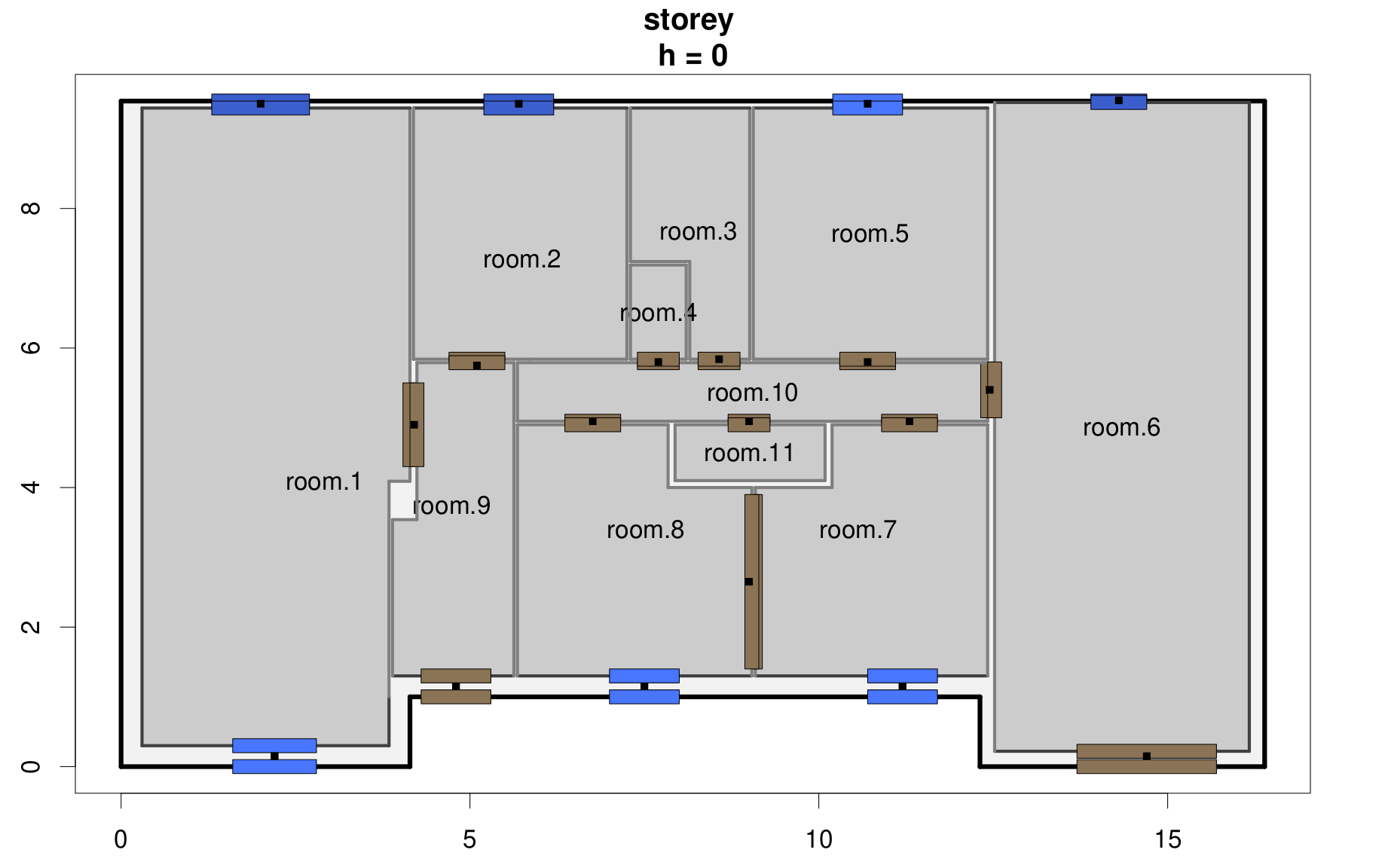
Building model
A building model describes all the characteristics that are necessary to determine the quantity and disposition of the elementary components present in the building:
- the geometry of the building, which is a description in three dimensions of its shape, including all its openings;
- the composition of the building, which refers to the building materials;
- the contents of the building, which refers to the nature and location of the equipment and stocks located in the building.
Figure 1 shows an example of a building model which represents a dwelling.

Geometry of the building
The geometry of a building is described as follows:
- the elevation of the building is given;
- the building is divided into storeys, made up of rooms;
- each storey is defined by the following characteristics:
- its elevation, which is relative to the one of the building;
- external walls, which define the external contour of the storey;
- rooms, which make up the storey;
- each room is defined by the following characteristics:
- its elevation, which is relative to the one of the storey. This elevation is used to locate the floor of the room;
- the height of the ceiling. This height, combined with the elevation of the room, is used to locate the ceiling of the room;
- the walls that define the contour of the room;
- each wall is defined by the following characteristics:
- its elevation, which is relative to the one of room. It is only used for external walls if they are below or above the floor;
- the positions of the starting and ending points of the wall. They are used to precisely locate the wall and to calculate the surface of the wall and related components;
- the openings that are present on this wall (may be empty);
- its coating (may be empty);
- each opening is defined by the following characteristics:
- its elevation, which is relative to the one of the wall where the opening is located;
- its height and width;
- its position of its middle point. This is used to check that openings are well positioned (an opening should not protrude from the wall on which it is located);
- each coating is defined by the following characteristics:
- its elevation, relative to the wall where it is located;
- its height. This is not a characteristic given by the user but computed depending on the other coatings that are present or on the height of the wall.
Composition of the building
The composition of the building refers to the elementary components that make up the built part of the building. These elementary components belong to the following types:1
- baseboard: it is defined by its constituent material. It is optional to include a baseboard;
- ceiling: three kinds of elementary components are associated to ceilings: the ceiling itself, the ceiling insulation, the ceiling coating. They are all defined by their constituent material. The ceiling insulation and coating are optional;
- coverstrip: it is defined by its constituent material. It is optional to include a coverstrip;
- floor: three kinds of elementary components are associated to floors: the floor itself, the floor insulation, the floor coating. They are all defined by their constituent material. The floor insulation and coating are optional;
- opening: it is defined by its constituent material and its subtype (door, window, french window). It is optional to include an opening;
- wall: three kinds of elementary components are associated to walls: the wall itself, the wall render, and the wall insulation. The wall is defined by its constituent material and its subtype (load bearing wall, partition, or lining). The wall render and insulation are defined by their constituent material;
- coating: it refers to the wall coatings and it is defined by its constituent material. Wall coatings are defined separately because they do not always share the geometry of their supporting wall;
Contents of the building
The contents of the building refers to the elementary components that compose:
- the equipment and stocks located in the building, if the building is used as an economic activity;
- the furniture of the building, if the building is used as a dwelling.
Each elementary component that is part of the contents is defined by the following characteristics:
- its name;
- the name of the room in which it is located;
- the name of wall on which it is located (optional);
- its elevation, which is relative to the one of the room in which it is located;
- the dilapidation that must be applied to take its age into account when calculating its value. The default value for the dilapidation is 50%;
- the quantity in which it is present in the building;
- its minimum and maximum replacement values;
- some details on its nature (optional).
Protection of the building
A building model can include a protective device to limit the damage due to floods. If present, this protective device is defined at the building level and has the following characteristics:
- type: indicates whether the device is external (protecting both the interior and the exterior of the building, as flood barriers may do) or internal (protecting only the interior of the building, and openings, as slot-in flood barriers may do);
- elevation: indicates the relative water depth for which the device is designed;
- duration: indicates the flood duration for which the device is designed;
- reliability: indicates the reliability of the protective device.
Footnotes
If it is not specified that a type of component is optional, it is mandatory to include it to produce a model of building.↩︎